Amazon has officially rolled out a comprehensive new web interface for Alexa, enabling users to control smart home devices, manage routines, and interact with the voice assistant directly from any web browser, marking a significant expansion of Alexa's accessibility.
Introduction (The Lede)
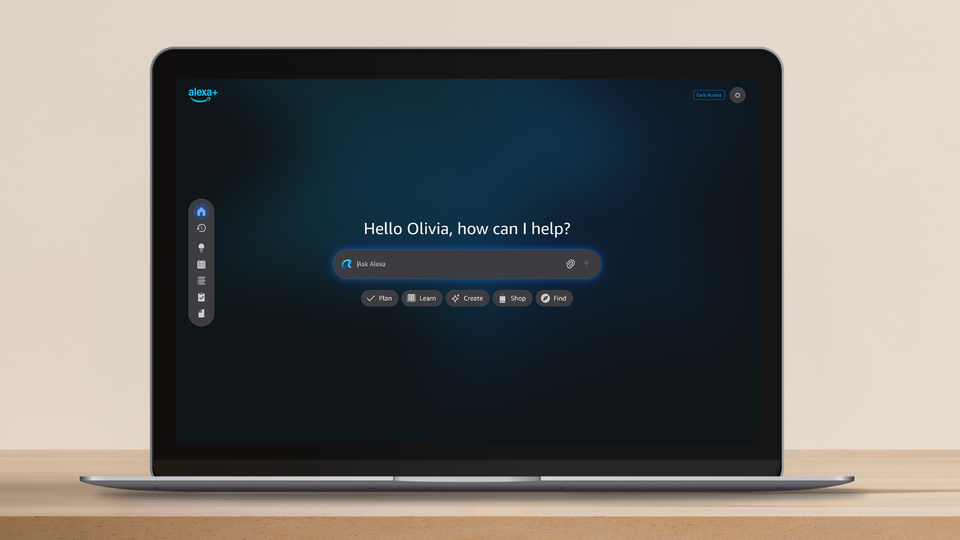
Amazon is significantly extending the reach and accessibility of its Alexa voice assistant by launching a comprehensive new web interface. This strategic move allows users to interact with Alexa directly through any web browser, offering a visual and tactile way to manage smart home devices, create routines, and access Alexa's full suite of features without needing a dedicated Echo device or a smartphone. The rollout, which began in early May 2024, transforms Alexa into an even more ubiquitous digital assistant.
The Core Details
The newly unveiled Alexa web interface provides a robust platform for interacting with the assistant from any internet-connected computer. Designed to mirror much of the functionality found in the Alexa mobile app, this web app is now rolling out globally.
- Access: Users can access the full Alexa experience by navigating to their regional Alexa domain (e.g., alexa.amazon.com) through any modern web browser.
- Key Features: The interface allows for comprehensive smart home device control and management, creation and modification of custom routines, and direct access to shopping lists, to-do lists, and reminders.
- Interaction Methods: Users can issue commands and queries through both typing and, where supported by the browser and user permissions, voice input.
- Visual Feedback: Unlike purely voice-based interactions, the web interface offers a rich graphical user interface (GUI) that provides visual feedback for commands and displays information clearly.
- Cost: The web app is a free extension of the existing Alexa service, requiring no additional subscription or purchase.
Context & Market Position
Historically, Amazon's Alexa, much like Google Assistant and Apple's Siri, has primarily been tethered to dedicated hardware—smart speakers, displays, and smartphones. While a rudimentary web portal for Alexa existed prior to this update, its capabilities were largely limited to device setup and basic skill management, offering little in terms of interactive daily use. This new web interface fundamentally alters Alexa's market position, evolving it from a device-centric assistant to a truly platform-agnostic service.
This move directly addresses a significant user convenience gap, enabling individuals to manage their smart home ecosystem or engage with Alexa's features from their computer without the need to switch devices or verbally address an Echo speaker. In comparison to competitors, while Google Assistant offers some web-based smart home control via its search interface and dedicated apps, a comprehensive, dedicated web application providing a full assistant experience is less common. Apple's Siri, conversely, remains largely ensconced within its proprietary ecosystem. By transcending its hardware origins, Amazon is positioning Alexa as a versatile, omnipresent digital companion, accessible wherever an internet browser is present.Why It Matters (The Analysis)
The introduction of a full-fledged Alexa web interface carries substantial implications for both consumers and the broader smart home industry. For consumers, the immediate benefit is unparalleled convenience and accessibility. Users can now seamlessly control their smart home devices, manage calendars, and create routines from any computer, eliminating the need to have an Echo device nearby or constantly reach for their smartphone. This is particularly valuable in environments like offices, public spaces, or shared homes where speaking commands might be impractical or undesirable. It also caters to users who prefer a visual interface for managing complex settings or who find typing commands more intuitive than speaking. This ubiquitous access deepens user engagement with the Alexa ecosystem, making it an indispensable part of their digital life, irrespective of their physical location or device.
For Amazon and the smart home industry, this is a strategic play to solidify Alexa's dominance and expand its reach beyond traditional hardware sales. By making Alexa accessible across virtually any internet-connected device with a browser, Amazon broadens its user base and lowers the barrier to entry for new adopters. It reinforces Alexa's utility and value proposition for existing users, potentially driving further adoption of Alexa-enabled smart home devices and services. This move also sets a significant precedent for how voice assistants can evolve beyond pure voice interaction, embracing multimodal input methods (typing, clicking, voice) and offering a richer, more flexible user experience. Ultimately, it strengthens Amazon's smart home ecosystem, making it more resilient and pervasive.
What's Next
This expansion signals Amazon's clear commitment to evolving Alexa into a truly pervasive and multimodal assistant. Looking ahead, we can anticipate further refinements and enhancements to the web experience, potentially including deeper integration with desktop applications and more sophisticated browser-based interactions, such as richer media playback or advanced productivity features. This move blurs the lines between dedicated mobile apps and web services for smart assistants, suggesting a future where digital helpers are seamlessly integrated into every aspect of our digital lives, accessible and adaptable to any context or device.